Edited by Jack Herrick, Edge, Syndi B, Krystle C. and 127 others
Are you learning to grow your own sweet, juicy
tomatoes? Luckily for you, tomato plants can grow almost anywhere, that
is warm and a little damp. But as with most vegetation that produce a
fruit, a little "tender, loving care" or TLC goes a long way. With
adequate sunlight, water, and patience, you'll be greatly rewarded with a
six foot tall tomato plant with big red juicy tomatoes! Tomatoes take a
long time to grow so you must have great patience. That's all you need
to do to get your tomato plant growing. Have fun growing!

|

Tomato Disease Identification Key by Affected Plant Part: Leaf Symptoms
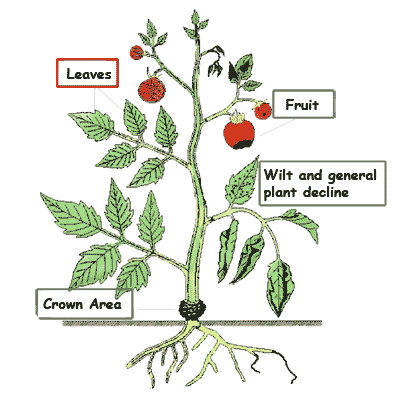
Generalized tomato plant adapted from Plant
Pathology 4th edition by G. N. Agrios copyright 1997 as Figure 1-1
published by Academic Press, San Diego, CA, with permission from
Elsevier.
Guía sinóptica para hoja de tomate en espanol.
| Leaf Symptoms by pathogen groups or other causes |
|
|
Oomycetes
|
Viruses
|
Viroids
|
|
Phytoplasma
|
Physiological/Weather
|
Damage from
|
|
|
|
|
Nutritional disorders
|
|
|
Leaf Symptoms
Black or dark brown spots usually circular and varying in size (see individual characteristic symptoms to fine tune diagnosis
|
Symptoms
|
Disease
|
Characteristic symptoms
|
Other parts affected
|
 |
Bacterial
speck |
tiny, dark brown to black spots with surrounding yellow halo |
fruit, stem |
 |
Bacterial
spot |
small dark brown to black circular spots, initially water-soaked, coalescing and becoming angular, may have yellow halo |
fruit, stem |
|
Syringae leaf spot |
brown spots with and without a halo, appearing similar to bacterial speck |
fruit, stem |
 |
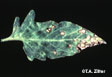
Early
blight |
initially appears a irregular lesions
on oldest mature leaves near the ground; lesions expand, becoming dark
brown and necrotic with concentric black rings giving a target-like
appearance; may have a chlorotic area surrounding lesion |
fruit, stem, whole plant |
 |
Septoria
leaf spot |
initially small circular water-soaked
spots beginning on older leaves; spots enlarge in diameter with a black
or brown border and with gray centers that are speckled with small black
fruiting bodies |
stem, whole plant |
 |
Gray leaf spot |
small brownish lesions becoming irregular and often
surrounded by chlorotic areas; lesion will dry up and develop cracks;
southern states |
whole plant |
 |
Target spot |
initially as tiny lesions, expanding with yellow halos; lesions coalesce leading to collapse of tissue; southern states |
fruit, stem |
 |
Tomato
spotted wilt virus |
tiny irregular brown spots, streaks, and ring spots usually on the youngest leaves; southern states |
fruit, stem,
whole plant
|
Marginal browning of leaf tissue, with necrotic spots and irregular interveinal lesions later in disease development
|
Symptoms
|
Disease
|
Characteristic symptoms
|
Other parts affected
|
 |
Bacterial
canker |
brown margin with yellow border to inside; characteristically the leaves remain attached to the plant |
fruit, stem, whole plant |
Chlorotic lesion on upper surface, sporulation on lower surface
|
Symptoms
|
Disease
|
Characteristic symptoms
|
Other parts affected
|
 |
Leaf mold |
light yellowish areas on upper surface corresponds
with olive-brown fungal masses on lower surface; primarily a greenhouse
disease and taken to the field on transplants |
fruit, stem |
| |
Powdery mildew (Leveillula) |
yellow lesions on the upper surface
with a light powdery fungal sporulation on the lower surface; typically
found in dryer western states |
stem |
Broad irregular water-soaked lesion turning dark brown or beige with white sporulating growth during wet weather
|
Symptoms
|
Disease
|
Characteristic symptoms
|
Other parts affected
|
 |
Late blight |
large water-soaked lesions which become
black with white sporulation on the margin of lesion, usually on lower
surface but occasionally on upper leaf surface; appear beige in color
once lesions dry out in hot weather |
fruit, stem, whole plant |
Broad irregular lesion with gray fungal sporulation
|
Symptoms
|
Disease
|
Characteristic symptoms
|
Other parts affected
|
 |
Gray mold |
light brown spots, often start at wound
or dead tissue; fuzzy gray fungal growth when moist; common in
greenhouse production when poorly ventilated |
fruit, stem, whole plant |
Zonate shaped lesions during wet weather
|
Symptoms
|
Disease
|
Characteristic symptoms
|
Other parts affected
|
 |
Zonate spot
(Cristulariella) |
light tan lesions with distinct concentric rings;
occurs during wet weather and could be confused with late blight;
associated with nearby infected box elder and black walnut trees |
fruit, stem |
Whitish fungal growth mainly circular or upper surface
|
Symptoms
|
Disease
|
Characteristic symptoms
|
Other parts affected
|
 |
Powdery
mildew (Oidium) |
white, powdery fungal growth appears on
upper and lower leaf surface; typically a greenhouse problem, but can
be taken to the field on transplants |
stem |
Yellowing, necrosis and wilting of leaves
|
Symptoms
|
Disease
|
Characteristic symptoms
|
Other parts affected
|
 |
Bacterial
canker |
brown marginal lesions and later
developing interveinally as irregular lesions; yellowing leaves on
wilting plants, remain attached to stems |
fruit, stem, whole plant |
 |
Bacterial pith necrosis |
yellowing and wilting of leaves, blacking and enlarging of petioles and nodes, and progressing to top of plant |
stem, whole plant |
| |
Fusarium foot rot (F. solani) |
interveinal chlorosis and necrosis of leaves later turning brown |
stem, roots, whole plant |
| |
Fusarium crown and root rot (F. oxysporum f. sp. radicis-lycopersici) |
yellowing of older leaves and progressing to top of plants after mature green fruit stages |
stem, roots, whole plant |
| |
Fusarium wilt (F. oxysporum f. sp. lycopersici, 3 races) |
begins as yellowing of oldest leaves,
and progressing upward, often with yellowing on one side of leaf or
branch; brown vascular tissue in stem at crown and above |
stem, roots, whole plant |
 |
Verticillium
wilt
|
yellowing with a V-shaped pattern turning brown with brown vascular tissue inside stem at crown of plant |
stem, roots, whole plant |
Yellowing and bronzing, or calico with stunting
|
Symptoms
|
Disease
|
Characteristic symptoms
|
Other parts affected
|
 |
Tomato
spotted wilt virus |
as the full manifestation of disease develops (see above), leaves will also show yellowing and bronzing |
fruit, stem, whole plant |
 |
Alfalfa mosaic virus |
yellowing and purpling develops on mature plant leaves, while calico symptoms appear on young leaves |
fruit, stem, whole plant |
Fernleaf appearance or symptoms as green mottling
|
Symptoms
|
Disease
|
Characteristic symptoms
|
Other parts affected
|
 |
Cucumber mosaic |
leaves are susceptible at all stages, but symptoms
can consist of mottling and severe fernleaf or “shoestring” appearance;
occurrence of satellite viruses can greatly modify symptoms |
fruit, stem, whole plant |
Leaf distortion and mottling
|
Symptoms
|
Disease
|
Characteristic symptoms
|
Other parts affected
|
 |
Tobacco etch |
leaves are susceptible at all stages; symptoms consist of mottling and leaf distortion |
fruit, stem, whole plant |
  |
Potato virus Y |
faint mottling and slight distortion along with
veinbanding mosaic; field symptoms include dark brown dead areas; other
necrotic strains reported |
fruit, stem, whole plant |
Chlorotic mottling or fernleaf under cool growing conditions
|
Symptoms
|
Disease
|
Characteristic symptoms
|
Other parts affected
|
 |
Tobacco (tomato) mosaic |
common strains cause mottled areas of light and
dark green on the leaves; aucuba strains cause yellowing; leaves also
may exhibit leafrolling and fernleaf-like symptoms |
fruit, stem, whole plant |
Dark brown streaks on foliage, stems, fruit
|
Symptoms
|
Disease
|
Characteristic symptoms
|
Other parts affected
|
 |
Tobacco mosaic & Potato virus X-double streak |
mixture of two viruses prompts dark brown to black streaks with downward leaf curl |
fruit, stem, whole plant |
Leafroll, marginal yellowing and rugosity
|
Symptoms
|
Disease
|
Characteristic symptoms
|
Other parts affected
|
 |
Potato leafroll |
leaf rolling and marginal leaf chlorosis |
fruit, stem, whole plant |
Leafroll, but without yellowing or rugosity
|
Symptoms
|
Disease
|
Characteristic symptoms
|
Other parts affected
|
 |
Physiological leafroll |
pronounced leafroll of foliage over most of plant |
whole plant |
Plant stunting, rugosity and leaf distortion
|
Symptoms
|
Disease
|
Characteristic symptoms
|
Other parts affected
|
 |
Tomato planta macho |
stunting, apical proliferation, leaf narrowing, chlorosis, necrosis, crinkling and brittleness of leaf tissue |
fruit, stem, whole plant |
 |
Tomato bunchy top |
see above |
fruit, stem, whole plant |
 |
Tomato apical stunt |
see above |
fruit, stem, whole plant |
Big bud of flower parts
|
Symptoms
|
Disease
|
Characteristic symptoms
|
Other parts affected
|
 |
Tomato big bud |
leaves are small, distorted and yellowish green |
fruit, stem, whole plant |
Green callus-like growth on upper and lower surface
|
Symptoms
|
Disease
|
Characteristic symptoms
|
Other parts affected
|
 |
Edema |
green callus-like growth on both the upper and lower leaf surface; tissue may tear as leaf matures as shown in illustrations |
|
Insect related injury; virus-like or herbicide-like damage (plant growth regulator or toxin)
|
Symptoms
|
Pest
|
Characteristic symptoms
|
Other parts affected
|
 |
Silverleaf whitefly |
both adult and nymphal stages have piercing-sucking mouthparts that cause spotting and later chlorosis |
fruit |
 |
Broad mite |
symptoms on tomato and potato appear similar with
leaf necrosis, particularly along the veins on the underneath surface
with rugosity and stunting of terminal leaf growth. |
|
Virus-like symptoms caused by herbicides
|
Symptoms
|
Disease
|
Characteristic symptoms
|
Other parts affected
|
 |
2,4-D (Phenoxy) |
extent of damage depends upon dosage received; growth distortion and fernleaf-like symptoms |
fruit, stem, whole plant |
 |
Glyphosate (Roundup, Phosphono amino acids) |
extent of damage is illustrated and depends upon
dosage received; terminal epinasty with fernleaf distortion, yellowing
and necrosis and stunting, or bright yellowing |
fruit, stem, whole plant |
Insecticide injury
|
Symptoms
|
Disease
|
Characteristic symptoms
|
Other parts affected
|
 |
Malathion (insecticide) |
classical pesticide burn on upper and lower leaf surface, free of any fungal growth, unless secondaries have invaded tissue |
fruit, stem, whole plant |
Nutrient deficiencies
|
Symptoms
|
Disease
|
Characteristic symptoms
|
Other parts affected
|
 |
Magnesium |
chlorosis and chlorotic blotches later becoming necrotic |
whole plant |
 |
Iron |
yellowing between veins and rare on mature leaves |
whole plant |






















































No comments:
Post a Comment